Manually Invoking Express.js Middleware Functions
The other day, I experimented with porting Framework One (FW/1) concepts into an Express.js web application. I love the class-based organization and inversion of control (IoC) that FW/1 offers; and, I wanted to see if something similar could be built on top of the middleware-based control flow that Express.js provides. In that experiment, I ended-up building all of the FW/1 life-cycle hooks as middleware functions because the whole next()-based callback mechanism felt very magical - like a blackbox. In order to peer into that blackbox, I wanted to further experiment with invoking Express.js middleware functions manually. This way, I may have more options in how I consume Express-compatible code going forward.
At its core, Express.js is just a stack of functions that gets called in series. In fact, it's easy to think about Express.js request handling like a Promise chain. Each middleware function in Express.js acts like a resolution handler (if it has 3 arguments) or a rejection handler (if it has 4 arguments). And, just like a Promise chain, each middleware function is capable of switching the request processing back and forth between a resolution and a rejection state (if you squint hard enough).
NOTE: Unlike a promise chain, Express.js middleware doesn't pass resolved values directly onto the next handler. Instead, Express.js middleware acts by augmenting the request and response objects.
So, if I want to invoke Express.js middleware functions manually, it makes sense to try and wrap their execution in a Promise chain, where each middleware function is proxied by an individual Promise callback. This way, the "next()" function that I pass into each middleware handler could act by moving the local Promise into a "resolved" or a "rejected" state. Which, by the way, is a utility function that basically all Node.js Promise libraries offer.
To experiment with this, I created a simple Express.js demo that has a single route handler. And, within that single route handler, I am manually invoking a series of middleware functions before rendering the final response. To do this, I am essentially reducing the collection of functions into a single Promise chain, which I then return to the calling context
| // Require our core node modules. | |
| var chalk = require( "chalk" ); | |
| var express = require( "express" ); | |
| var Q = require( "q" ); | |
| var _ = require( "lodash" ); | |
| // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // | |
| // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // | |
| // I complete in success, synchronously. | |
| function middlewareOne( request, response, next ) { | |
| console.log( chalk.red.bold( "[ONE]:" ), "running..." ); | |
| next(); | |
| } | |
| // I completely in error, synchronously. | |
| function middlewareTwo( request, response, next ) { | |
| console.log( chalk.red.bold( "[TWO]:" ), "running..." ); | |
| throw( new Error( "Two went boom!" ) ); | |
| } | |
| // I completely in error, asynchronously. | |
| function middlewareThree( request, response, next ) { | |
| console.log( chalk.red.bold( "[THREE]:" ), "running..." ); | |
| setTimeout( | |
| () => { | |
| next( new Error( "Three went boom!" ) ); | |
| }, | |
| 100 | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // | |
| // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // | |
| var app = module.exports = express(); | |
| // For this exploration, we only have one route to handle all requests. But, as an | |
| // experiment, the route handler will explicitly invoke the middleware functions as a | |
| // means to demystify how the middleware works. | |
| // -- | |
| // NOTE: I am NOT RECOMMENDING that you do this in your Express.js application - I am | |
| // doing this because next() feels a bit too magical and I want to make it mundane. And, | |
| // because I have reasons to want to be able to run it explicitly from within other | |
| // middleware instances. | |
| app.get( | |
| "/", | |
| function ( request, response, next ) { | |
| console.log( chalk.green.bold( "Processing:" ), request.path ); | |
| // Let's define the collection of middleware to invoke explicitly. | |
| // -- | |
| // NOTE: I am creating an arbitrary array structure to test the flattening. | |
| var middlewares = [ | |
| middlewareOne, | |
| [ | |
| middlewareTwo, | |
| // Since we know that TWO will throw an error, we'll catch it with error | |
| // handling middleware and turn it back into a "resolved" chain. | |
| function catchTwo( request, response, error, next ) { | |
| console.log( chalk.dim.italic( "Two threw an error:", error.message ) ); | |
| next(); | |
| }, | |
| [ | |
| middlewareThree, | |
| // Since we know that THREE will throw an error, we'll catch it with | |
| // error handling middleware and turn it back into a "resolved" chain. | |
| function catchThree( request, response, error, next ) { | |
| console.log( chalk.dim.italic( "Three threw an error:", error.message ) ); | |
| next(); | |
| } | |
| ] | |
| ] | |
| ]; | |
| // Now, let's manually run the collection of middleware and then pipe the | |
| // control flow back into the current request resolution. | |
| invokeMiddleware( middlewares ) | |
| .then( | |
| () => { | |
| console.log( chalk.red.bold( "[REQUEST]:" ), "closing..." ); | |
| response.send( "Hello world" ); | |
| } | |
| ) | |
| .catch( next ) | |
| ; | |
| } | |
| ); | |
| // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // | |
| // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // | |
| // I invoke the given middlewares and return a promise. | |
| // -- | |
| // NOTE: Internally, Express.js DOES NOT USE PROMISES for the middleware; as such, | |
| // using promises will add some performance overhead and a forced asynchronous control | |
| // flow whereas the core middlware may run synchronously. | |
| function invokeMiddleware( middlewares, request, response ) { | |
| var promise = _ | |
| // Express automatically collapses all of the middleware into a flat array. As | |
| // such, we want to flatten the given collection before we reduce it. | |
| .flattenDeep( [ middlewares ] ) | |
| .reduce( | |
| ( chain, handler ) => { | |
| // If the handler accepts four explicit arguments, it is an error handler; | |
| // append it to the promise chain as a catch(). | |
| if ( handler.length === 4 ) { | |
| var tail = chain.catch( | |
| ( error ) => { | |
| return( invokeHandler( handler, [ request, response, error ] ) ); | |
| } | |
| ); | |
| // Otherwise, if the handler accepts three explicit arguments, it is a | |
| // normal handler; append it to the promise chain as a then(). | |
| } else if ( handler.length === 3 ) { | |
| var tail = chain.then( | |
| () => { | |
| return( invokeHandler( handler, [ request, response ] ) ); | |
| } | |
| ); | |
| // If the handler accepts an unexpected number of arguments, just bypass | |
| // it, passing the existing chain onto the next handler. | |
| } else { | |
| var tail = chain; | |
| } | |
| return( tail ); | |
| }, | |
| Q.when() // Initial promise chain. | |
| ) | |
| ; | |
| return( promise ); | |
| // I wrap the given handler invocation in a promise. | |
| function invokeHandler( handler, handlerArgs ) { | |
| var deferred = Q.defer(); | |
| // NOTE: We don't need to worry about synchronous errors during invocation | |
| // because the handler is already being invoked inside of the Promise handler | |
| // in the above reduction. | |
| handler.call( null, ...handlerArgs, deferred.makeNodeResolver() ); | |
| return( deferred.promise ); | |
| } | |
| } |
As you can see, the collection of middleware is composed of an arbitrarily nested array. I did this simply because Express.js allows it and I wanted to build that into my invocation strategy. This array is then flattened and reduced into a Promise chain. If the given middleware has three arguments, I treat it like normal middleware and fold it into the Promise chain as a .then() handler. And, if the given middleware has four arguments, I treat it as an error handler and fold it into the Promise chain as a .catch() handler.
If we bootup this Express.js application and make a request to it, we get the following terminal output:
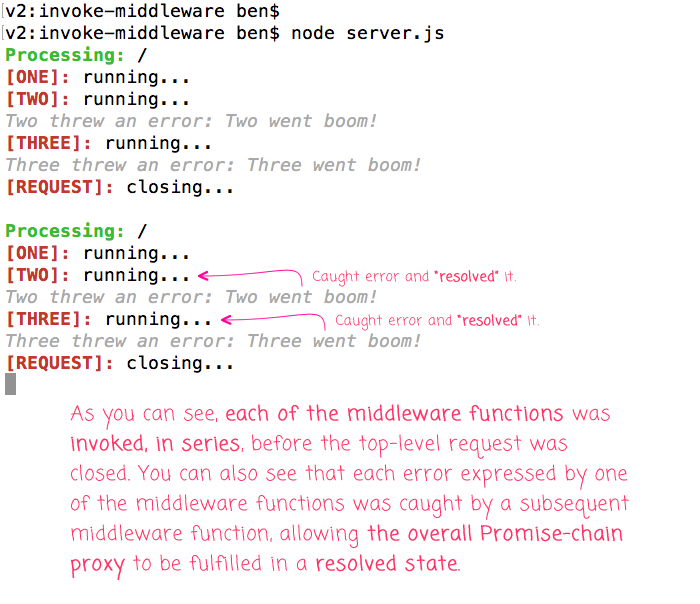
As you can see, each of the middleware was successfully invoked - manually - from within my one Express.js route handler. And, each of the error handlers was able to successfully catch the thrown error and convert the Promise chain wrapper back to a resolved state so that our top-level router handler could successfully complete the request.
To be clear, I am not recommending that people start invoking Express.js middleware manually. Middleware makes sense as "middleware". I just wanted to experiment with this because I can think of some situations in which I may want to leverage existing middleware functions in a context where the middleware architecture has been abstracted away from direct use. And, if nothing else, I feel that experiments like this make Express.js and middleware seem like less of a blackbox, which is good for the old mental model.
Want to use code from this post? Check out the license.
Reader Comments
@All,
For what it's wroth, Scott Rippey on my team had a thought that this approach would be helpful for unit-testing middleware since you wouldn't need to spin up / mock-out an entire Express app just see if the inputs / outputs of middleware make sense.
@All,
CAUTION: I just realized that my *** ERROR *** object is in the wrong parameter location. It is supposed to be in the FIRST parameter, but I am passing it as the THIRD. In my demo, it happens to work because I am manually invoking the handler (so I basically messed it up on both sides of the call-stack).